Abstract
Amniotic fluid (AF) possesses anti-inflammatory, anti-microbial and regenerative properties that make it attractive for use in clinical applications. The goals of this study were to assess the feasibility of collecting AF from full-term pregnancies and to evaluate non-cellular and cellular properties of AF for clinical applications. Donor informed consent and medical histories were obtained from pregnant women scheduled for C-sections and infectious disease testing was performed the day of collection. AFs were evaluated for total volume, fluid chemistries, total protein, and hyaluronic acid (HA) levels. AF was also assessed with quantitative antibody arrays, cellular content and for an ability to support angiogenesis. Thirty-six pregnant women consented and passed donor screening to give birth tissue. AF was successfully collected from 17 individuals. Median AF volumes were 70 mL (range 10–815 mL; n = 17). Fluid chemistries were similar, but some differences were noted in HA levels and cytokine profiles. Cytokine arrays revealed that an average of 304 ± 20 of 400 proteins tested were present in AF with a majority of cytokines associated with host defense. AF supported angiogenesis. Epithelioid cells were the major cell type in AF with only a minor population of lymphoid cells. Cultures revealed a highly proliferative population of adherent cells capable of producing therapeutic doses of mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). These findings showed that significant volumes of AF were routinely collected from full-term births. AF contained a number of bioactive proteins and only a rare population of MSCs. Variations noted in components present in different AFs, warrant further investigations to determine their relevance for specific clinical applications.
Effect of Amniotic Fluid Stem Cells and Amniotic Fluid Cells on the Wound Healing Process in a White Rat Model
Bioelectric Stimulation + Amniotic Fluid in Diabetic Foot and Leg Ulceration
Purpose
| Condition | Intervention |
|---|---|
| All Subjects Will Receive Best Medical Therapy. Those Randomised to Device Will Additionally Use the Device | Device: VascuStim bioelectric stimulator deviceBiologic: Amniotic fluid membraneOther: Best Medical Therapy |
| Study Type: | Interventional |
| Study Design: | Allocation: Randomized Intervention Model: Parallel Assignment Masking: Open Label Primary Purpose: Treatment |
| Official Title: | Bioelectric Stimulation + Amniotic Fluid in Diabetic Foot and Leg Ulceration |
Primary Outcome Measures:
- Ulcer healing [ Time Frame: 16 weeks ]
Time to 50% healing of leg ulcer, as measured by volume (3D camera)
Secondary Outcome Measures:
- Quality of life [ Time Frame: 16 weeks ]
Improvement in quality of life questionnaire values, comparing baseline to 6 weeks with treatment
| Target Enrollment: | 300 to 1200 patients |
| Expected Study Start Date: | October 2017 |
| Expected Study Completion Date: | December 2018 |
| Primary Completion Date: | December 2018 (Final data collection date for primary outcome measure) |
| Arms | Assigned Interventions |
|---|---|
| Active Comparator: No device
Treated with best medical therapy
|
Other: Best Medical Therapy
Seen in outpatient clinic for wound care and ongoing advice
|
| Experimental: Device + Biologic
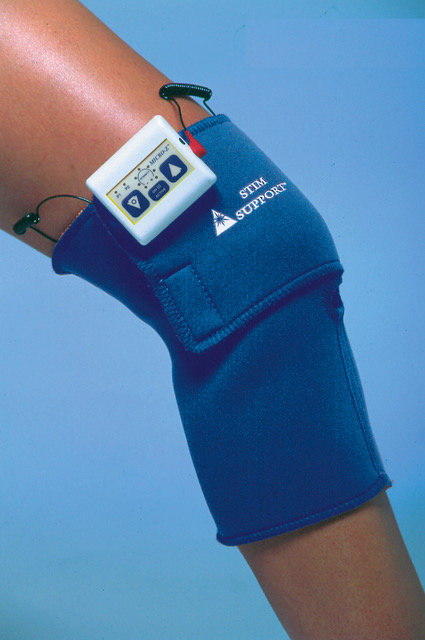
As well as receiving best medical therapy, these people will be given the VascuStim device therapy via stimulation electrodes applied on their affected leg. They will be stimulated for 2 hours every three days during a 16 week course of treatment. Amniotic fluid membranes will be placed on all wounds with renewed application every ? days.
|
Device: VascuStim bioelectric stimulator device
Placed on the lateral aspect of the knee, when activated it causes the leg to twitch + amniotic fluid membrane placed on wounds
Other: Best Medical Therapy Seen in outpatient clinic for wound care and ongoing advice
|
 Eligibility
Eligibility
| Ages Eligible for Study: | 18 Years and older (Adult, Senior) |
| Sexes Eligible for Study: | All |
| Accepts Healthy Volunteers: | No |
- 18+ years old
- Type 2 diabetes on best medical therapy
- Active foot ulceration, present <3 months Exclusion criteria
- Pregnancy
- Pacemaker
- Metal implants in the legs (below knee)
 Contacts and Locations
Contacts and Locations
Choosing to participate in a study is an important personal decision. Talk with your doctor and family members or friends about deciding to join a study. To learn more about this study, you or your doctor may contact the study research staff using the Contacts provided below. For general information, see Learn About Clinical Studies.
Please refer to this study by its ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: ***********
| Principal Investigator: |
 More Information
More Information
| Responsible Party: VascuStim a Leonhardt Ventures Co. | |
| ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: | |
| Other Study ID Numbers: | |
| Study First Received: | |
| Last Updated: |
Additional relevant MeSH terms:
| Diabetic Foot Foot Ulcer Diabetic Angiopathies Leg Ulcer Skin Ulcer Diabetic Neuropathies Vascular Diseases |
Cardiovascular Diseases Skin Diseases Diabetes Complications Diabetes Mellitus Endocrine System Diseases Foot Diseases |
Supporting Articles
Vascular Klotho Deficiency Potentiates the Development of Human Artery Calcification and Mediates Resistance to Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 – Click Here
Effects of electrical stimulation therapy on the blood flow in chronic critical limb ischemia patients following regenerative therapy – Click Here
Therapeutic efficacy of sonic hedgehog protein in experimental diabetic neuropathy – Click here
Effective Wound Healing Enabled by Discrete Alternative Electric Fields from Wearable Nanogenerators – Click Here
Electrical stimulation promotes the angiogenic potential of adipose-derived stem cells – Click Here
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Release Following Electrical …
Electrical stimulation (ES) is a well-documented treatment used to assist the healing of chronic wounds. … Thus, it is believed that the application of an exogenous electrical current may mimic the body’s own bioelectric currents and reinitiate or facilitate the wound repair process.
Innovation
www.aetna.com/cpb/medical/data/600_699/0680.html
Aetna considers electrical stimulation for the treatment of chronic ulcers in the …. in the treatment of chronic and painful venous leg ulcers in 20 older patients.
Electrical stimulation to accelerate wound healing – NCBI – NIH
Sep 16, 2013 – Keywords: diabetic foot ulcer, electric stimulation therapy, treatment … delayed wound healing and higher bacterial counts in leg ulcers.
Electrical Stimulation and Cutaneous Wound Healing: A Review of …
Oct 27, 2014 – Keywords: electrical stimulation, electrobiofeedback, wound healing, ….. for the treatment of 47 patients with leg and diabetic foot ulcers [42].
Effect of electrical stimulation on chronic leg ulcer size and appearance.
Phys Ther. 2003 Jan;83(1):17-28. Effect of electrical stimulation on chronic leg ulcer size and appearance. Houghton PE(1), Kincaid CB, Lovell M, Campbell KE,
E-Stimulation: An Effective Modality to Facilitate Wound Healing …
www.todayswoundclinic.com/e-stimulation-effective-modality-facilitate-wound-healing
May 9, 2012 – When it comes to chronic wounds, electrical stimulation (ES), one of …. Effect ofelectrical stimulation on chronic leg ulcer size and appearance.
Effect of Electrical Stimulation on Chronic Leg Ulcer … – Oxford Academic
Abstract. Background and Purpose. Electrical current has been recommended for use on chronic pressure ulcers; however, the ability of this modality to improve .
A current affair: electrotherapy in wound healing – NCBI – NIH
Apr 20, 2017 – The effect of electrical stimulation (ES) has been tested in vitro on different … vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the blood during the stimulation ….. Asadi MR, Torkaman G. Bacterial inhibition by electrical stimulation. … Evaluation of electrical stimulation for ischemic wound therapy: a feasibility …
The Effect of Microcurrent Electrical Stimulation on the Foot … – J-Stage
stimulation on the foot blood circulation and the degree of pain experienced by diabetes patients. … microcurrent electric stimulation of the foot may be helpful for preventing the … angiogenictherapy9,10). …. 9) Kanno S, Oda N, Abe M, et al.
Asadi Angiogenic effects of low-intensity cathodal direct current
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence
VASCSTIM CLINICAL
VASCSTIM CLINICAL PROTOCOL
Background:
Peripheral arterial disease (PAD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Recent data has shown that it has become the leading cause of hospital readmission and results in XXX,000 amputations each year. The most common cause of PAD is diabetes, which can cause conduit vessel disease, but more commonly results in occlusion of the microvasculature. This microvascular form of PAD, is not very responsive to current surgical or catheter based revascularization therapy. It typically results in non-healing ulcers once a skin breakdown occurs, despite the use of several current treatment options including hyperbaric oxygen and various dressings. Non-healing ulcers results in significant morbidity, but also significant health care costs which have been recently estimated at over $xx million/year.
These data provide the stimulus for identification of new treatment options. Two of the most promising are use of low current Bioelectric Stimulation (BES) and amniotic fluid and membranes(AF) in patients with or without the diagnosis of diabetes.
GOAL:
The goal of this registry is to document the ability of the combination of BES and AF in improve the size and depth of non-healing ulcers due to PAD.
Description: This is a prospective, non-randomized, non-blinded, interventional, consecutive series Registry study to determine initial safety and efficacy of a series of treatments with bioelectric stimulation controlled protein expression followed by use of AF as a membrane laid onto the ulcer, with or without additional use of injected AF around the ulcer in the treatment of non-healing skin ulcers of leg or foot due to PAD.
The study, including the protocol and consent form will have been approved without stipulations by a local or certified Institutional Review Board as meeting safe and good clinical practice before any subject will be enrolled.
Inclusion Criteria:
- Age 18-80 yrs of age
- Non-healing skin ulcer of leg or foot > 2 cm in diameter
- Able to tolerate up to 40 minutes of BES on the non-involved leg or foot
- Able and willing to make the required study visits.
- Able and willing to give informed consent and follow study instructions.
- Must speak, read, and understand English
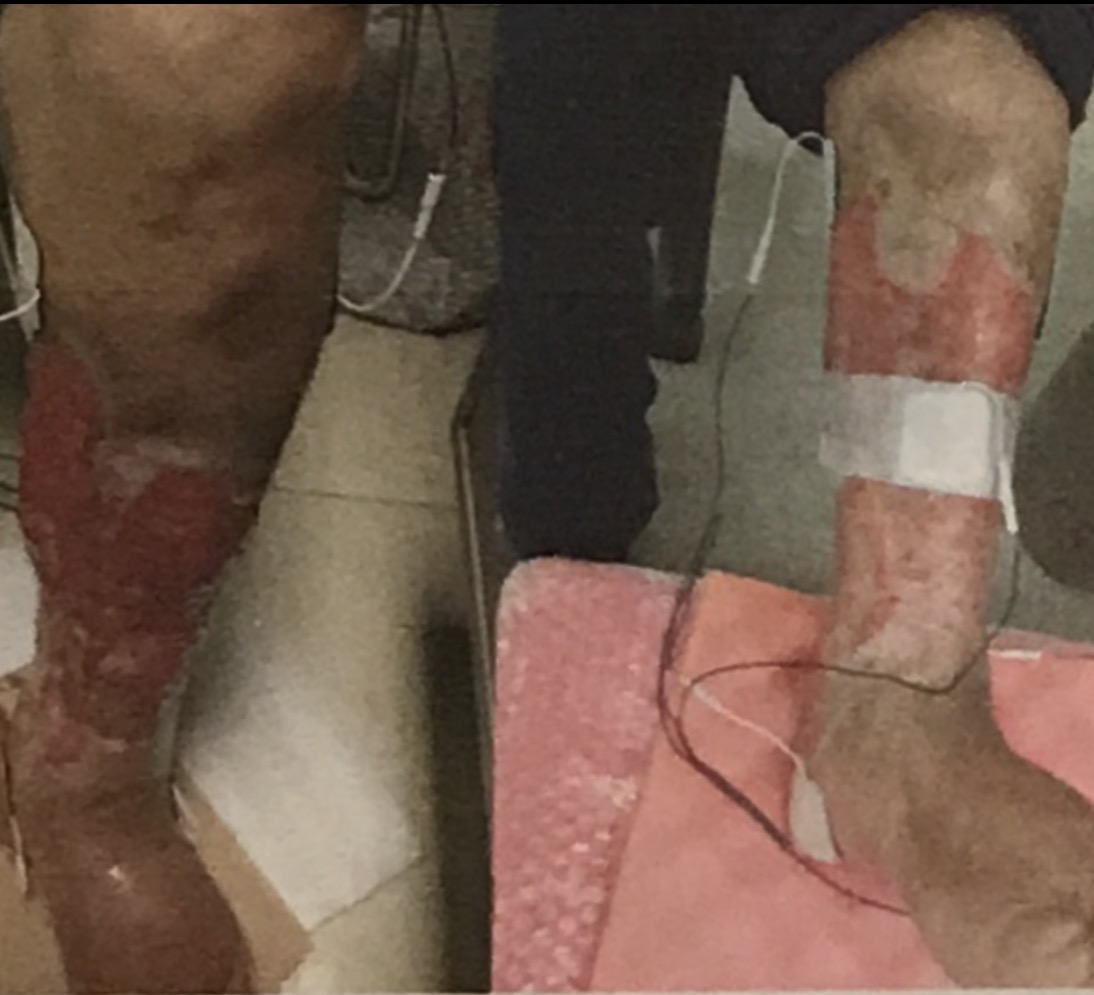
- Agree to allow photographs to be taken of the ulcer before and at the end of the treatment period to document change.
Exclusion Criteria:
- Use of concomitant treatments to improve wound healing, including topical medications, oral medications, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, non-ablative fractional laser treatment, low-level laser therapy, PRP injection within the preceding 2 months.
- Allergic to lidocaine or epinepherine
- Planned revascularization procedure in next 3 months
- Individuals with diminished decision-making capacity
- Renal replacement therapy
- Pregnancy or lactating period for females
Target Number of Participants: 300
Target Number of Enrolling Sites: 30
Screening:
Any subject with a non-healing ulcer of >2 cm in diameter who meet all Inclusion and Exclusion criteria will be eligible for participation. Each potential subject will have a brief history and examination performed by the Investigator, and if acceptable, will be provided with an overview of the Registry and then provided with the Consent Form. If they choose to participate, and sign the Consent form, they will be enrolled in the Registry.
Baseline Evaluation:
All potential enrollees will have been evaluated by a certified vascular surgeon or physician who stipulates that the patient has a significant ulcer of the foot or leg is not responsive to all common treatments.
Before the procedure, a baseline photo will be taken of the planned treatment ulcer to compare to the measurements at the end of treatment period of 12 weeks.
Intervention:
Screening Treatment Bioelectic Stimulator:
All participants will have two standard electrical conductive skin patches or electro acupuncture needles applied in the region near the ulcer and connected to a bioelectric stimulation signal generator that has been previously tested and proven to be capable of delivering the required current.
The stimulator is capable of transmitting specific signals will be applied first to the uninvolved leg or foot. It will run through up to a 40 minute cycle of protein release signals to stimulate the release/increased expression of a number of growth factors that have been extensively shown to stimulate both the growth of new blood vessels and recruitment of stem cells to enhance native wound healing, initially including: SDF-1, and transitioning through IGF-1, HGF, EGF, eNOS, VEGF, Follistatin, Tropoelastin, and Activin A+B. If well tolerated, the patient will be eligible to participate in the Registry and treatment of the involved leg or foot.
Treatment with Amniotic Membrane with or without Amniotic Fluid (AF) Injection:
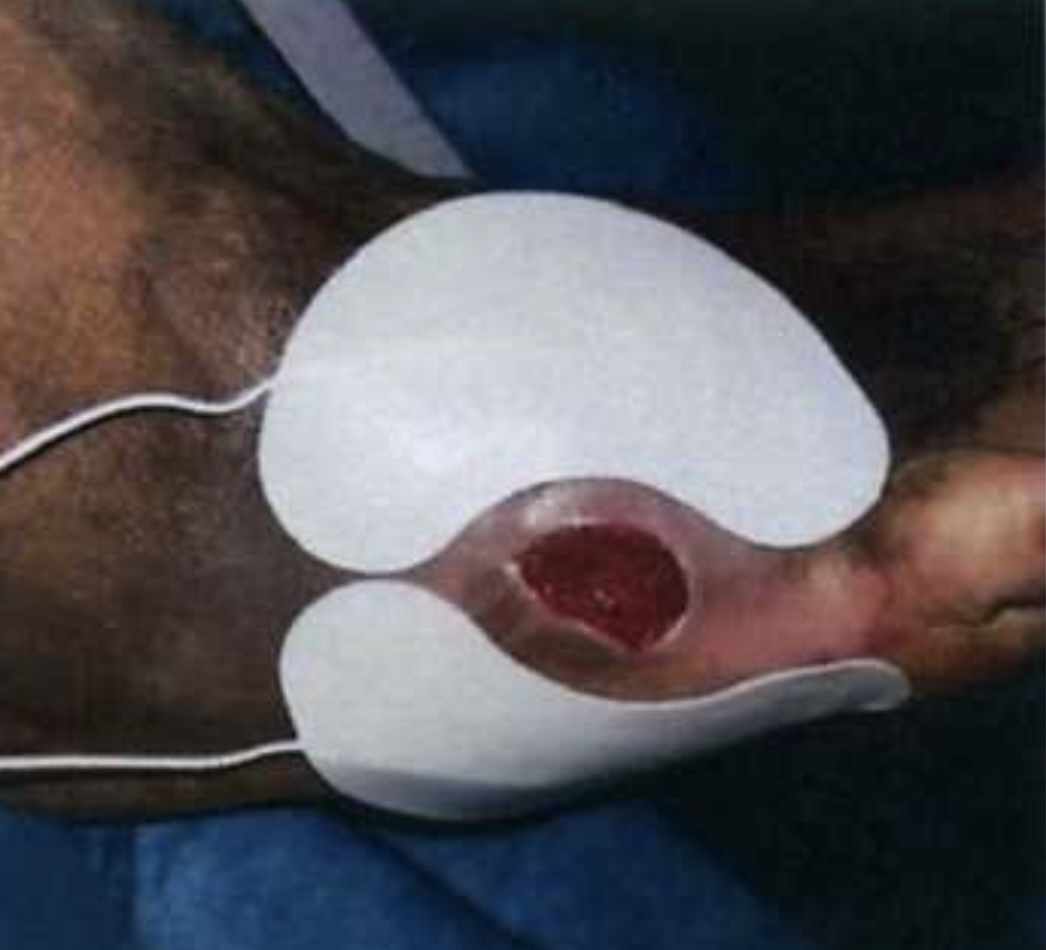
Each patient enrolled in the Registy will receive a single covering of the ulcer with an appropriate sized Amniotic Fluid Membrane, which will be provided by Bioleonhardt VASCSTIM, and reconstituted with several cc’s of Amniotic Fluid and laid directly onto the ulcer/wound.
The decision to also inject up to 5 cc’s of Amniotic Fluid will be made by the patient’s vascular surgeon or physician in advance of the treatment and injected at equal spacing into 8-10 sites approximately 2-3 centimeters from the edge of the wound in a circumferential pattern, with or without the use of lidocaine anesthesia at the patient’s choice.
A non-adhesive dressing will be applied over the Amniotic Membrane and wound at the completion of this treatment and a fresh dressing maintained over the wound for a minimum of 10 days, and then may remain uncovered at the discretion of the treating physician/
Treatment Schedule:
The treatments will take place for a period of 40 minutes, 3 times/week for 12 weeks to demonstrate the safety and benefit of the planned therapy.
Follow Up Evaluations:
At the end of 6 and 12 weeks, a photo will be taken of the wound being treated to measure and document the response to treatment.
The goal is complete healing of the wound by the end of the treatment.
Each subject will also have a brief interview inquiring about any adverse effects noted by the subject since enrolling in the Rtudy, and an examination by the Principal Investigator for any adverse effects of the therapy including damage or injury.
End Points:
Co-Primary Outcome Measure:
- Incidence of treatment-related adverse events by the end of the treatment period, to include, but not exclusively: local itching, bleeding, pain, swelling, local pain, or headache, visual changes, palpitations, or nausea, AND
- Percentage of wound healed by the end of the treatment period as assessed by quantitative measurement of the size of the wound.
Secondary Outcome Measures:
- Any adverse events not described above
- Incidence of need to terminate the study for pain or other cause
- Failure of the Bioelectric Stimulator
- Stopping Rules:
The Registry will be paused if a total of 3 of the study subjects experience a treatment-related side effect of at least moderate severity. It will be restarted when additional investigation yields a clear cause and effective action plan has been implemented.
Data Analysis:
Data will be collected for each patient and analyzed at three time points including the end of the first 100 patients, the end of 200 patients, and when the last enrolled individual has reached the 6 month post treatment time point. The Registry may be stopped if the data demonstrates a > 67 % complete wound healing at the end of the 12 week treatment period.
Additional subjects may be enrolled into the study if approved by the IRB and Sponsor.
Related Articles
Microcurrent as an adjunct therapy to accelerate chronic wound healing and reduce patient pain – Click Here
Anti-Aging β-Klotho Gene-Activated Scaffold Promotes Rejuvenative Wound Healing Response in Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells – Click Here
An mRNA sequencing analysis of the healing-promoting role of electroacupuncture a in rat skin wound model – Click Here
Wound healing treatment by high frequency ultrasound, microcurrent, and combined therapy modifies the immune response in rats – Click Here
https://mikrostrom.com/microcurrent-for-chronic-wounds/?lang=en
Cell Therapy in Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia by Vaclav … – Issuu
Thus, oxygen tension plays several roles in the expression of different genes such as the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family and proangiogenic
Stromal-Cell-Derived Factor-1 (SDF-1)/CXCL12 as Potential Target of …
Dec 16, 2011 – In the Western world, peripheral vascular disease (PVD) has a high prevalence with … This review will focus on the role of the SDF-1/CXCR4 system in the … potentials of growth factors such as hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), … of two angiogenic factors, platelet-derived growth factor BB and FGF-2, which …
VascuStim – Leonhardt Ventures
VascuStim is a combination product of a bioelectric stimulator that controls release of SDF-1 (stem cell homing signal), IGF-1, EGF, HGF, PDGF, VEGF, eNOS, …
Human amniotic membrane grafts in therapy of chronic non-healing …
Jan 12, 2016 – Human amniotic membrane (HAM) has five layers: epithelium, basement membrane, compact layer, fibroblast layer and spongy layer.1 Epithelium is the inner layer, and it is facing amniotic fluid, whereas the outer, spongy layer is connected to the vascular chorion. Amniotic epithelium consists of a single …
Top five components of amniotic fluid stem cell therapy. – ADIMarket
Dec 9, 2017 – Number one is that there are a lot of growth factors in amniotic fluid. Well, what exactly is a growth factor? A growth factor is a natural substance that’s produced by the body that helps to promote repair and regeneration of your tissues. And it also signals to other cells to help differentiate and promote repair …